Delivery in 2-3 working days
Tinnitus: More than just ringing in the ears
Have you ever noticed a constant buzzing or ringing in your ears that just won't stop? This condition, known as tinnitus, affects many people worldwide and can take both short-lived and chronic forms. Find out what tinnitus is, how it develops, and what treatments are available below.
What is tinnitus?
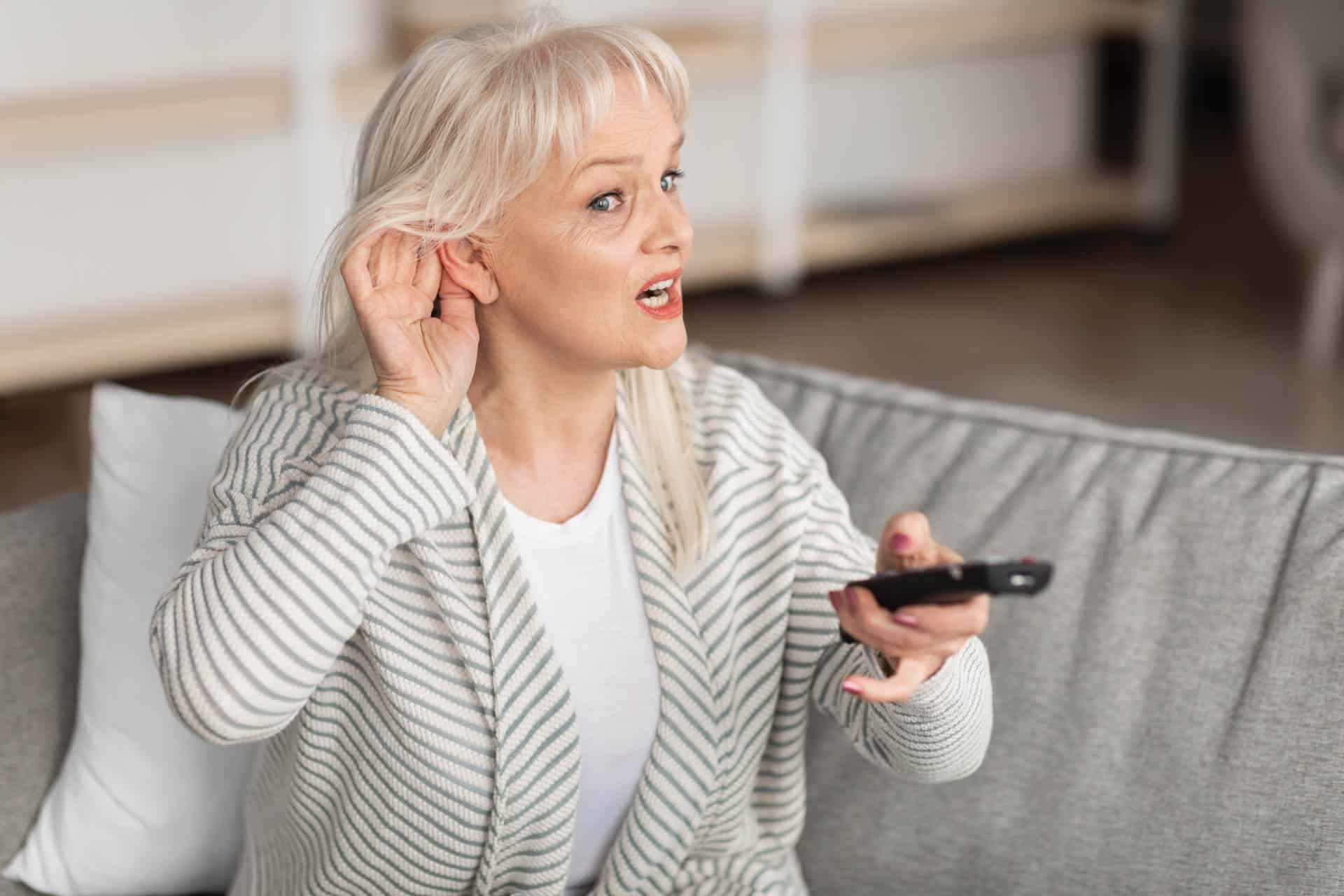
Tinnitus is a common disorder that causes ringing in the ears that can only be perceived by the sufferer. These sounds can seem like a buzzing, whistling, hissing or ringing and most often occur with hearing loss. In some people, it can also be perceived as a constant droning, clicking, or even music. Tinnitus is often the result of damage to the hair cells in the inner ear, which can be caused by a variety of factors, such as sounds that are too loud, certain medications, or even natural aging.
The role of the inner ear
The inner ear is crucial for our hearing and our perception of sounds. Hair cells in the inner ear help convert sound waves into electrical signals that our brain interprets as sounds. When these hair cells are damaged by noise, aging or certain diseases, signals can be sent incorrectly to the brain, resulting in tinnitus.
Symptoms and effects of tinnitus
Tinnitus can impact the lives of affected individuals in a variety of ways, and depending on the severity and duration of the tinnitus, the impact on daily life can vary significantly. Some of the most common symptoms of tinnitus are:

Continuous or periodic noise in the ear:
These ear noises can manifest as ringing, buzzing, hissing, whistling, or even music. They can occur in one or both ears and can be either constant or intermittent.
Difficulty hearing:
Many people with tinnitus also experience some form of hearing loss. The persistent ringing in the ears can make it difficult to hear external sounds clearly, which can make it difficult to understand speech.
Problems with sleep:
The constant noise in the ear can make it difficult to fall asleep or sleep through. This can lead to sleep deprivation and associated problems such as fatigue, irritability and difficulty concentrating.
Concentration problems:
The constant ringing in the ears can make it difficult for sufferers to concentrate on tasks, especially in quiet environments.
However, the effects of tinnitus go beyond the physical symptoms. For some people, tinnitus can cause significant psychological and emotional distress , including stress, anxiety, and depression. In severe cases, tinnitus can affect quality of life to the point that normal activities and social interactions are impaired.
Causes and risk factors
Tinnitus can result from a variety of causes, and it is important to understand these factors to determine the best approach for treatment and management. The following are some of the most common triggers and risk factors for tinnitus:
Noise pollution:
Both one-time loud noises and prolonged exposure to noise can lead to hearing damage and the development of tinnitus. In particular, occupations or hobbies that require regular exposure to high volumes, such as musicians, construction workers, or sports shooters, are associated with an increased risk of tinnitus. The use of headphones at high volume can also cause damage to the inner ear.
Aging process:
With advancing age, there is often a natural decline in the function of the hair cells in the inner ear, which can lead to hearing loss and, in many cases, tinnitus. This age-related hearing loss, also known as sensorineural hearing loss or presbycusis, affects about one-third of people between the ages of 65 and 75.
Medication:
Various medications can cause tinnitus as a side effect. These include certain antibiotics, cancer drugs, diuretics, certain antidepressants, and high doses of aspirin. In most cases, the tinnitus disappears when the medication is stopped or the dose is reduced.
Health problems:
Certain health conditions can also lead to tinnitus. These include conditions such as Meniere's disease, which is characterized by excessive fluid buildup in the inner ear, tumors in the ear, or hyperacusis, an increased sensitivity to normal environmental sounds. Conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes can also cause or exacerbate tinnitus.
Ear and head injuries:
Injuries to the head or ear can damage the inner ear and lead to tinnitus. This can be due to accidents, sports injuries or even aggressive ear cleaning.
It is important to note that in many cases, the exact cause of tinnitus cannot be identified. Therefore, it is critical to see a doctor if you experience persistent ringing in the ears to investigate possible causes and determine appropriate treatment options.
Hearing loss and tinnitus
For many people, tinnitus is accompanied by some form of hearing loss. It is estimated that over 90 percent of tinnitus patients also experience hearing loss. This can take the form of a high-frequency hearing loss, where the ability to hear high frequencies is impaired. In such cases, the sufferer may have difficulty hearing certain consonants and high-pitched sounds, making it difficult to understand conversations. This suggests a close relationship between tinnitus and damage to the inner ear, which is often responsible for hearing loss.
Diagnosis and treatment of tinnitus
Accurate diagnosis is critical for effective treatment of tinnitus. During the examination, an otolaryngologist may use the audiogram, a test that measures hearing across different frequencies.
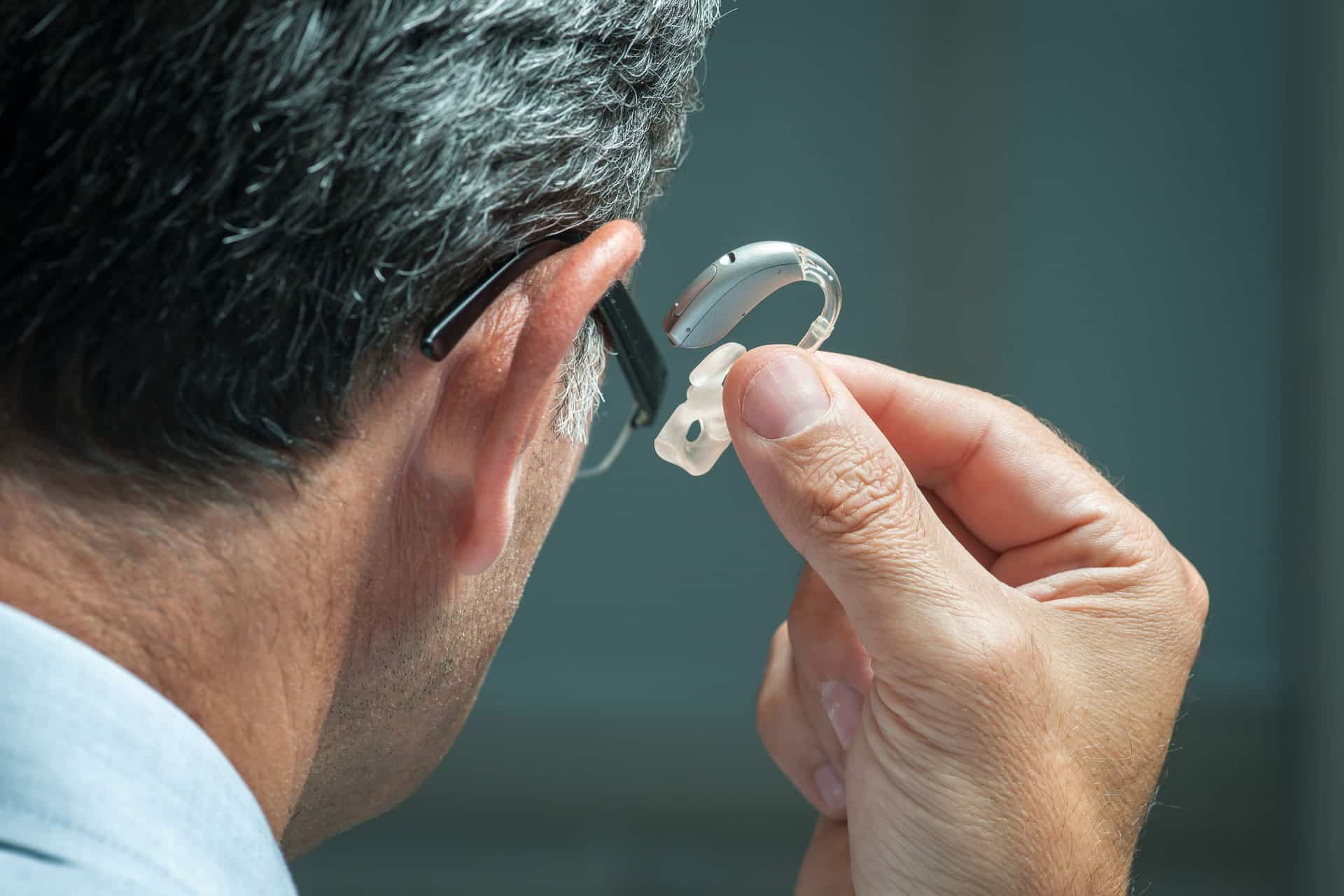
Treatment for tinnitus often focuses on treating the underlying cause. If hearing loss is the cause, hearing aids can help. Hearing aids can amplify the sounds around you, which helps drown out the ringing or buzzing in your ears. In some cases, noise and stress management therapy may be helpful.
Living with tinnitus
With the right support and treatment, people with tinnitus can lead normal and fulfilling lives. It is important to remember that everyone is different and there is no universal solution for tinnitus. What works for one person may not work for another. It is advisable to consult a medical professional to develop an individualized treatment strategy to manage tinnitus. Additionally, it may be helpful to learn stress management techniques to improve overall well-being.



